The Resistor Color Code Calculator serves as an essential tool for all users who need it, including both new learners and experienced professional engineers.
The combination of detailed instructions with a calculator tool allows users to quickly measure resistance values and tolerance and temperature coefficient of carbon-composition resistors in 4-band, 5-band and 6-band configurations.
The resistor color code system functions as a standardized method to indicate electrical properties of resistors through color markings.
The use of colors serves as the primary reason for this system. The majority of through-hole resistors exist as small cylindrical components. The space available on through-hole resistors makes it impossible to display complete value information such as "4,700 Ω ± 5%" because it would be too small to read. The colored band system provides a universal method to present electrical information which people can understand without needing to know the language.
The system provides users with direct access to three essential resistor properties.
The main value of a resistor is its resistance measurement which is expressed in Ohms (Ω). The acceptable error range which indicates precision levels for the resistor. The temperature coefficient (TCR) shows how resistance values change when temperatures fluctuate (found on 6-band resistors).
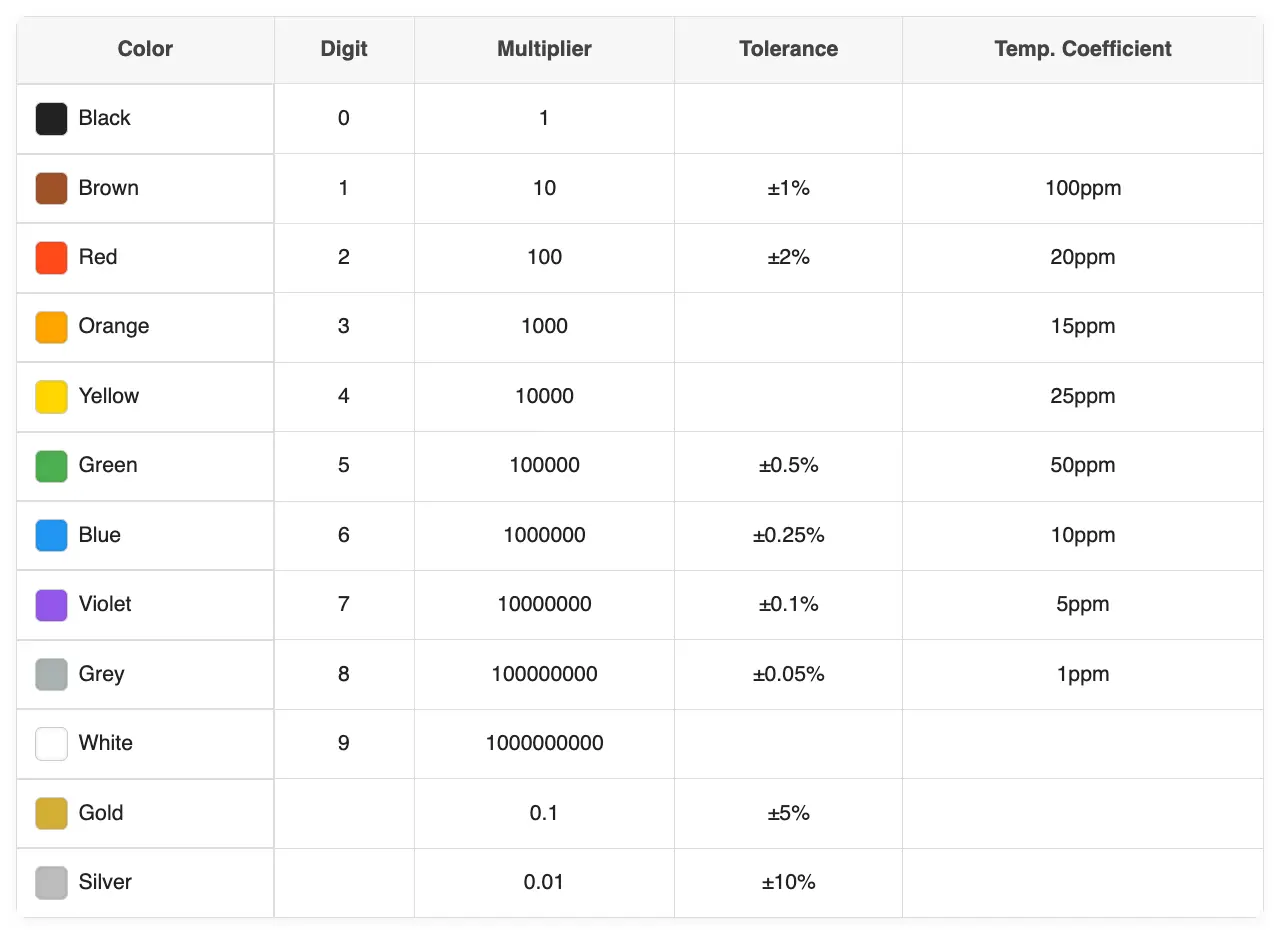
You must understand the meaning of each color band before you can read a resistor. The colors on resistors represent numbers and multipliers and tolerance values.
The following chart shows all the colors. The first ten colors can be remembered through the mnemonic "BB ROY Goes Britain Via Great Way" which stands for Black, Brown, Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Violet, Gray, White.
Different resistor types require specific methods to interpret their band patterns. The band interpretation pattern for resistors differs between 4-band and 5-band and 6-band configurations.
The additional digit in these resistors enables more precise value measurements.
The additional thermal stability band in these resistors operates similarly to 5-band resistors.
Our tool functions as a complete solution which removes all potential mistakes that users might make when reading resistor bands.
The tool presents a resistor image which users can interact with through the interface.
The Resistor Color Code Calculator together with these guidelines enables users to identify resistors accurately which leads to proper electronic circuit construction and operational success.